Salesforce Objects 101: A Comprehensive Handbook
An object in Salesforce is like an entity or table that contains data in rows and columns.
The row can be a record or tuple & column can be a field or attribute. Objects are used to store information in table form in the Salesforce database.
- Object ⇒ Table or entity
- Row ⇒ Record or tuple
- Column ⇒ Field or attribute
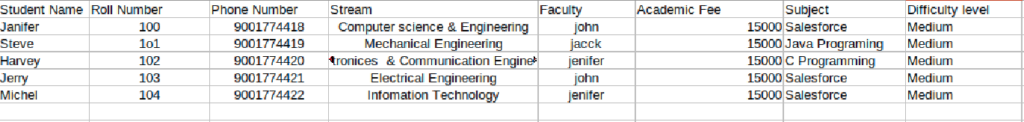
If you are not familiar with databases, think about storing data in a spreadsheet (CSV). For example, the Below table shows student data:
- Columns can store the Student name, Roll number, Phone number, Stream, Faculty, Fee, Subject, and Difficulty level attributes.
- Rows can store this information for each property that students have.
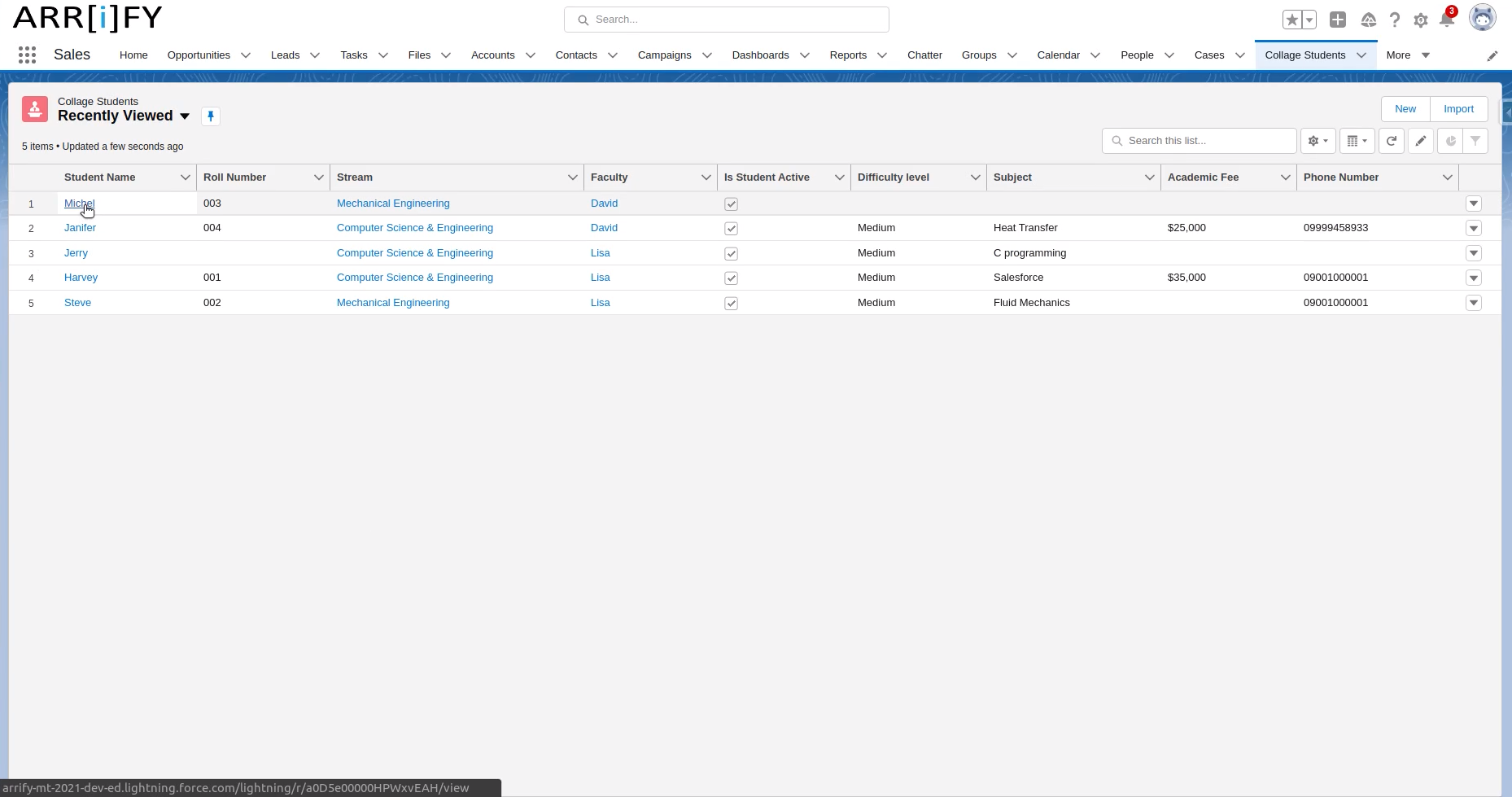
In Salesforce, we can think database tables as objects, columns as fields, and rows as records.
The above spreadsheet data, the User can store in the Salesforce by creating and using objects such as below :
Salesforce provides some standard objects that are already created for you, such as Account, Contact, Opportunity, and so on. Also, objects have built-in features i.e. User Interface, Security, Sharing model, etc.
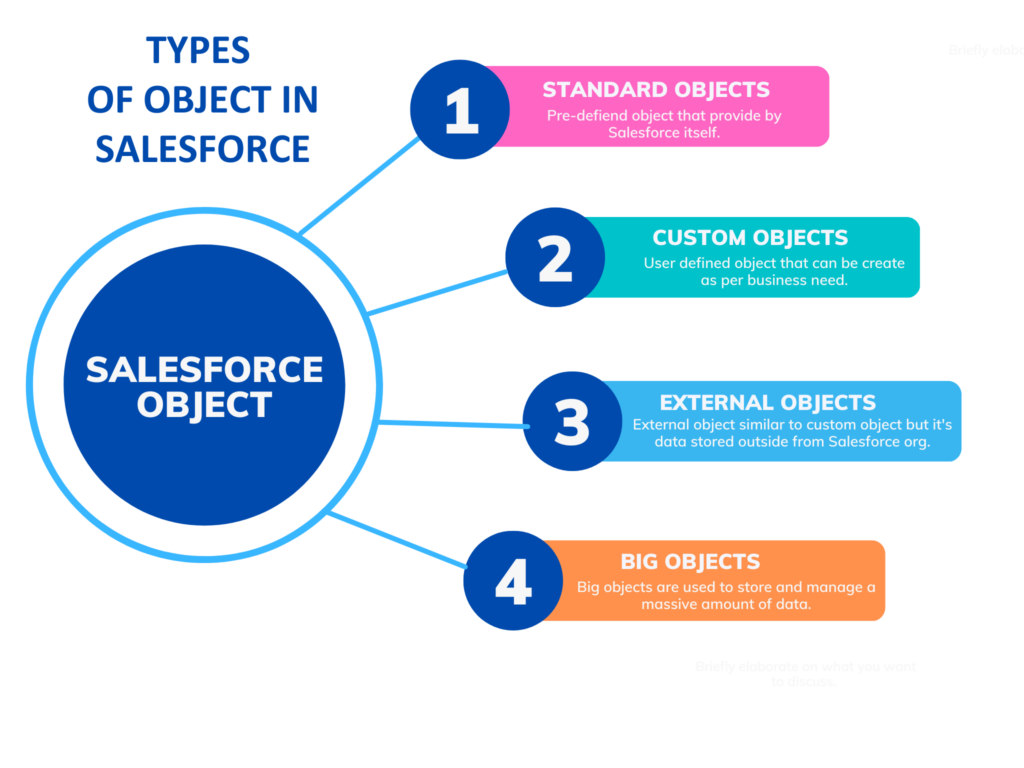
Types Of Objects in Salesforce
Here we discuss object types, their features, and limitations. In Salesforce we have mainly two types of objects, standard and custom objects, apart from these, we will also discuss the external and big objects.
Standard Objects in Salesforce
Standard objects are already created by Salesforce to use. Once you log into Salesforce, you can see the available standard objects. These include account, contact, opportunity, lead, campaign, and so on. The most commonly referred standard object is the Account Object. It is the object that stores the preliminary information about a customer, partner, competitor, or another organization.
Users cannot delete standard objects instead, salesforce allows users to create custom fields on standard objects.
List of Standard Objects in Salesforce:
- Account: Use to manage accounts or organizations.
- Asset: Use to track assets previously sold into customer accounts
- AccountPartner: A relationship between two Account objects such as partnerships
- AccountHistory: Represents the history of changes in the fields of an account
- AccountTeamMember: A User who is a member of an Account team
- Campaign: Use to manage brand marketing
- CampaignMember: The association between a Campaign and either a Lead or Contact
- Case: Use to manage cases for any organization
- case solution: The association between a particular Case and a particular Solution
- ChatterActivity: To represent the number of posts, likes, and comments made by a user
- Contact: An individual associated with an Account
- Contract: A business agreement associated with an Account
- Event: Manage calendar appointment event
- Group: A set of User records
- Lead: Store data of prospect or potential Opportunity
- Opportunity: Manage sale or pending deal
- Order: Represents an order associated with a contract or an account
- Pricebook: Contains the list of products that your organization sells
- Product: Product that an organization sells
- Profile: Defines a set of user permissions for performing different operations
- Quote: Manage proposed prices for products and services
- Report: Manage a set of data that meets certain criteria and is displayed in an organized way
- Solution: A detailed description of a customer issue and the resolution of that issue
- Task: An activity to perform or that has been performed
- User: To manage Salesforce user’s Data
- user license: Manage user license in the organization
Custom Objects in Salesforce
The organization’s data will always not fit into the existing standard objects. So we use custom objects for it. The objects created by users are called custom objects. Custom objects are the heart of any application.
Custom objects are very important to store different types of information in any organization. you can create custom objects according to requirements and manage org data easily. Custom objects are usually identified by a __c suffix.
Example of Custom Object: For example, a courier company can create a custom object to store the schedule and dispatch details for every week. So these objects store the data that is unique to the business.
External Objects
External objects are similar to custom objects. but external object record data is stored outside of your Salesforce organization. They allow us to map the data that’s stored outside your Salesforce organization. For example, You have data that is stored in the ERP system or any other place.
Salesforce Big Objects
When you have to manage a huge amount of data then you should use Salesforce Big Objects. These objects manage billions of records of data without compromising performance.
Big objects are used to store and manage a massive amount of data in Salesforce. Users can archive or bring massive datasets from outside systems into a Big object to get a full view of your customers. A big object provides consistence performance whether you have 1 million or more records.
You can’t use standard features of Salesforce like triggers, flows, and processes on Big Objects. Big objects are usually identified by a __b suffix.
What is Field in Salesforce?
In Salesforce, Fields represent exactly the same as what the columns represent in CSV files or any relational databases. Basically, it uses to store data values of records that are required for a particular object. A record is a set of fields value.
In Salesforce there are two types of fields that is standard field and custom field.
Standard Fields
Fields that are already present in Salesforce for standard and custom objects by default and cannot be deleted or edited.
Salesforce provides four standard fields in every custom object by default that are:
- Created By
- Last Modified By
- Owner and
- Created at the time of the creation of an object.
Custom Fields
The Custom fields are added by the user according to the business requirements of any organization. They may or may not be required.
Users can add different kinds of data depending on the requirements with help of fields data type which is available on field creation.
Data Types Of Fields
Each field in Salesforce has a defined data type. When these fields are created in Salesforce, the User has to choose their data type such as Text, Text Area, Number, PickList, etc. In the above table, we categorized some of the fields’ data type and their properties.
| Data Type | Property |
|---|---|
| Lookup Relationship | Create a relationship that links an object to another object. |
| Master-Details Relationship | Create a special type of parent-child relationship between two objects. |
| Checkbox | Allows users to select a True or False value. |
| Date | Allows users to enter or pick a date from a popup calendar. |
| Date/Time | Allows users to enter or pick a date with the current time from a popup calendar. |
| Allow user to enter email. | |
| Text | Allows users to enter any combination of letters and numbers. |
| Text Area | Allows users to enter up to 255 characters on separate lines. |
| Text Area (Rich) | Allows users to enter formatted text, and add images and links. Up to 131,072 characters on separate lines. |
| Formula | A read-only field that derives its value from a formula expression you define. |
| Currency | Allows users to enter a dollar or other currency amount and automatically formats. |
| Geolocation | Allows users to define locations. Includes latitude and longitude components. |
| Phone | Allows users to enter any phone number. |
| Picklist | Allows users to select a value from a list you define. |
| URL | Allows users to enter any valid website address. |
| Roll-Up Summary | A read-only field that displays the sum, minimum, or maximum value of a field in a related list or the record count of all records listed in a related list. |
| Picklist (Multi-Select) | Allows users to select multiple values from a list you define. |
How To Create Custom Object & Fields In Salesforce
Create Custom Object & Fields
Total Time: 10 minutes
Go to object manager in Setup
After going to set up, go to object manager then create a custom object.
Fill in custom object details & Save
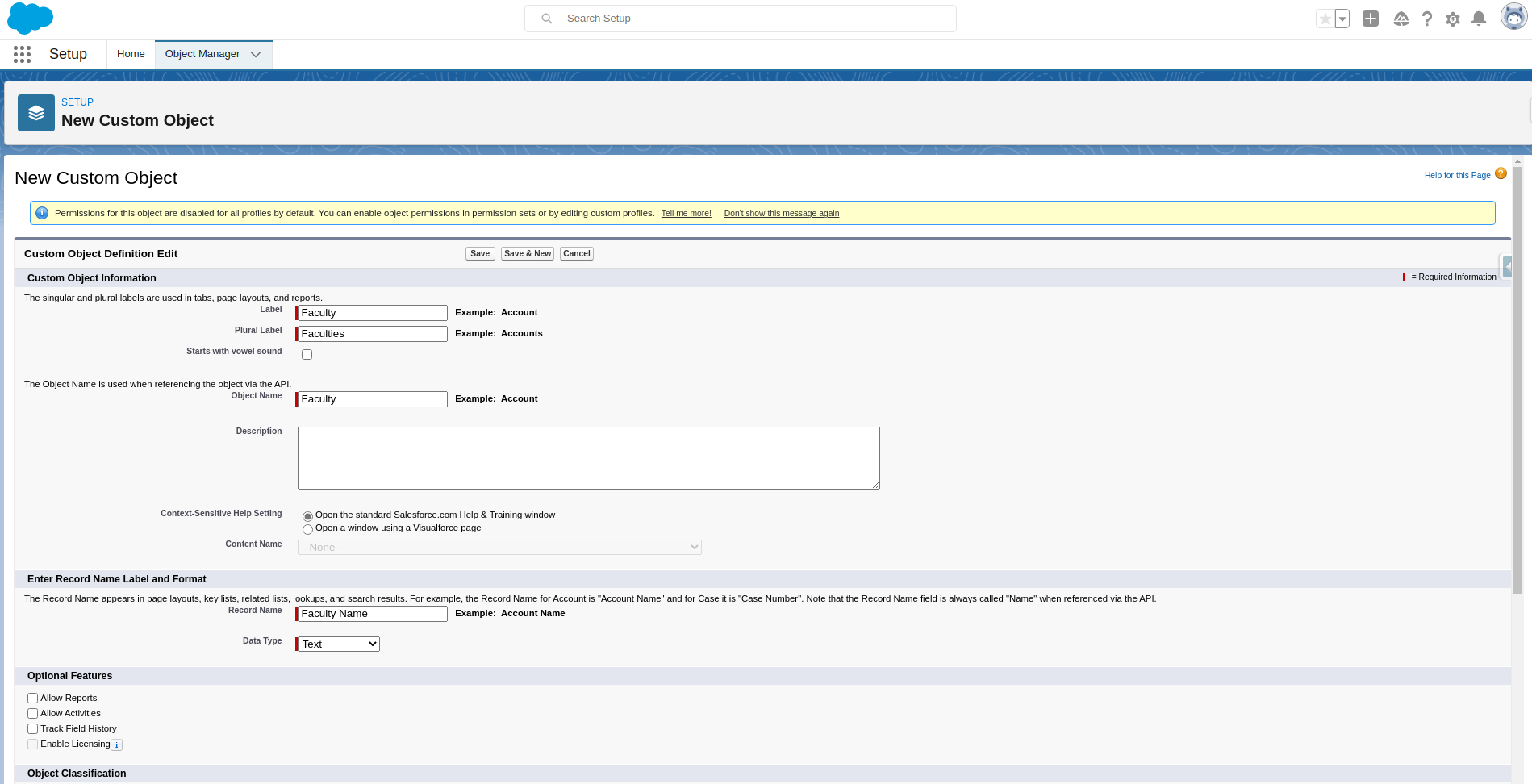
Fill in all required details about the custom object and click on save. We have the following optional features while creating an object.
Allow reports: If we check this check box, then only these objects are available to create reports.
Allow Activities: If we check this check box, then we can create activities on this object.
Track Field History: If we check this check box then only we are to track fields. We can track up to 20 fields for a single object.
In development: If we check this check box, this object is still in development mode. This object is not available for deployments.
Deployed: After selecting this check box then only it will be available for deployment.
Object created
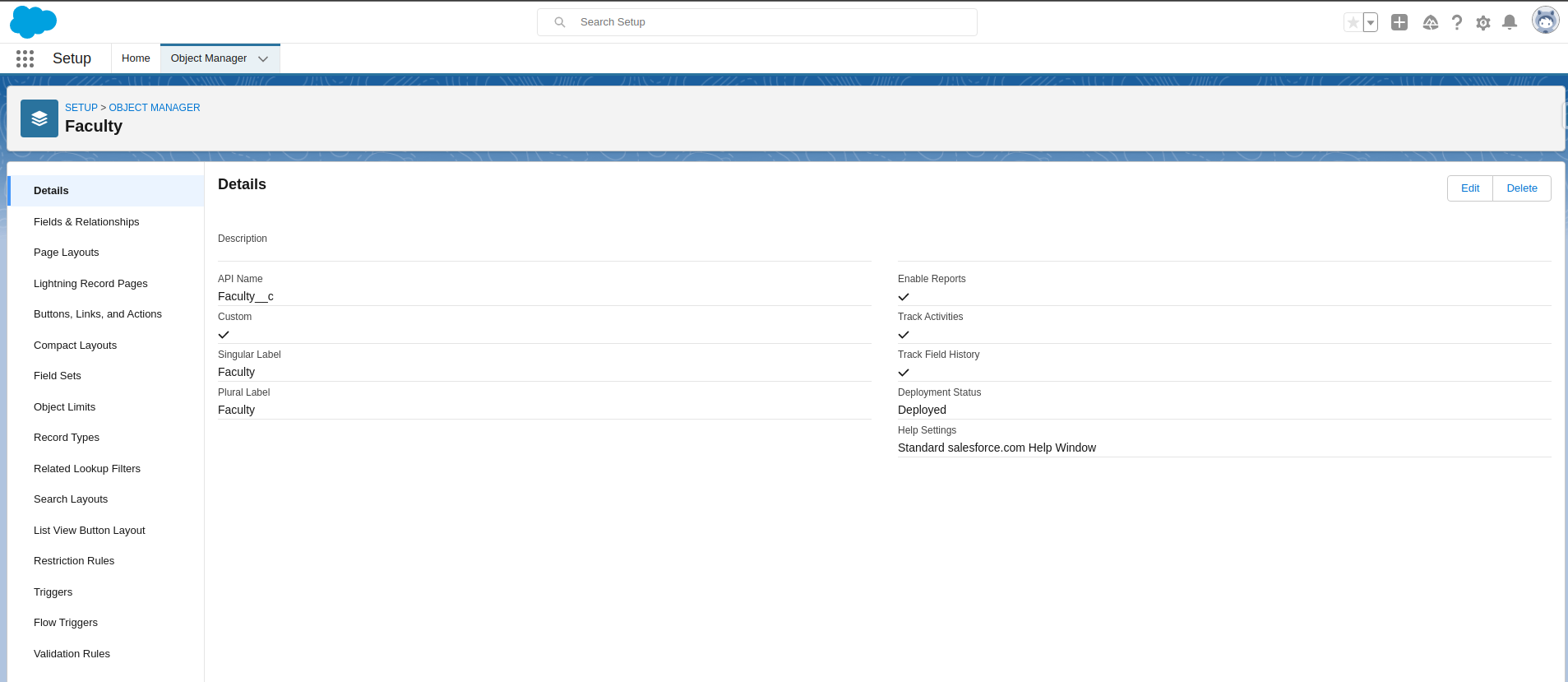
Object successfully created and on the left side, you can find its properties.
To add fields in the object
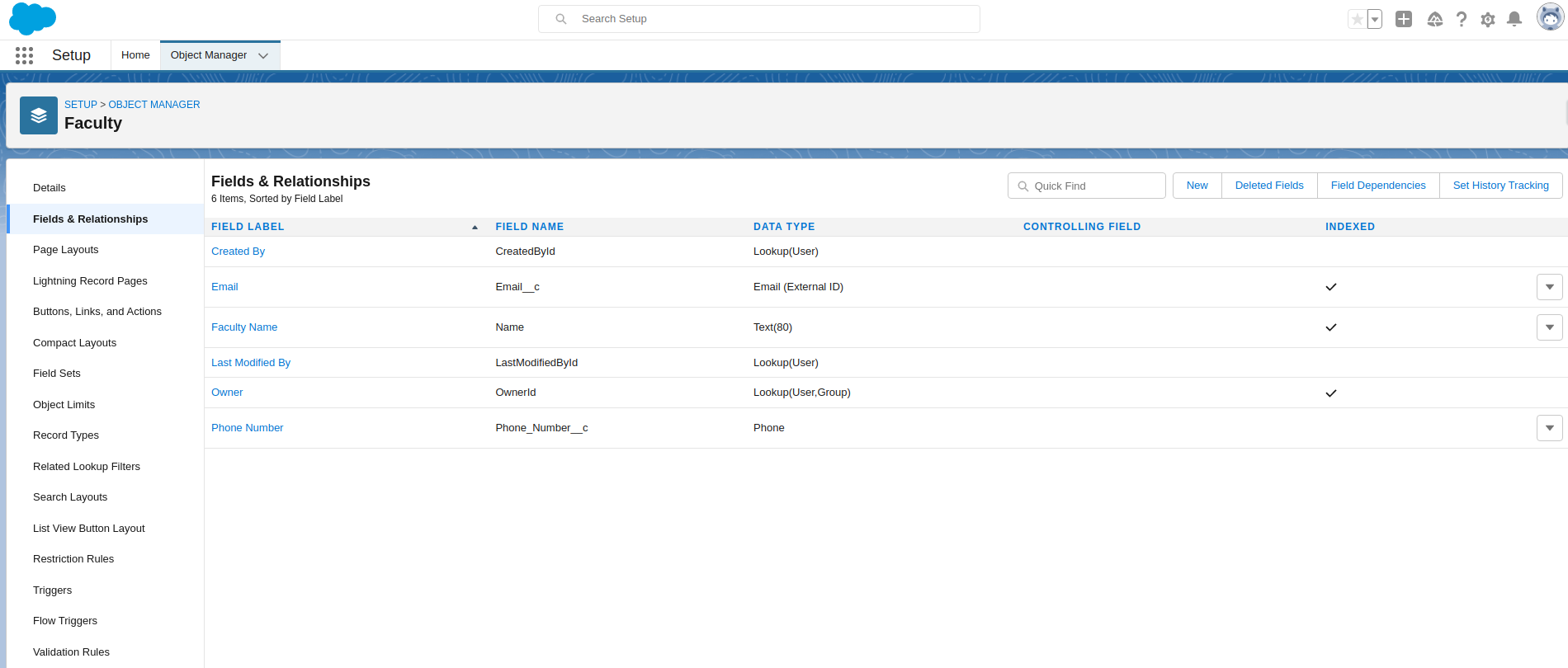
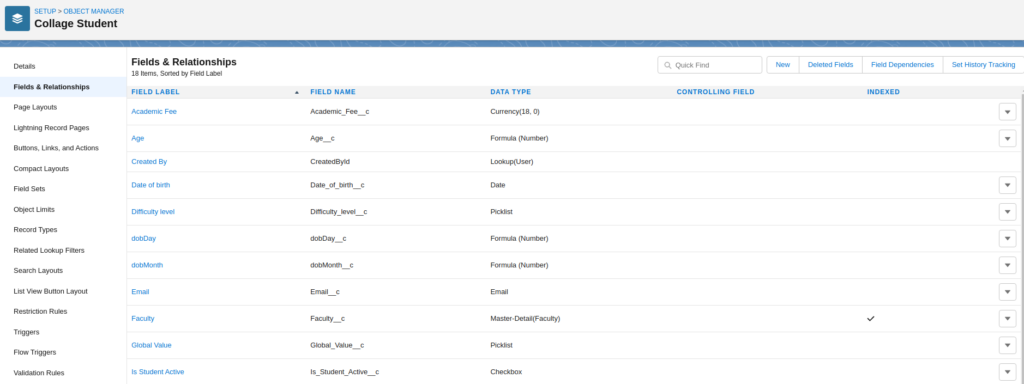
To add fields in an object, Go to object manager and find an object, Now open it and select Field & Relationships
Click on New To Create Field
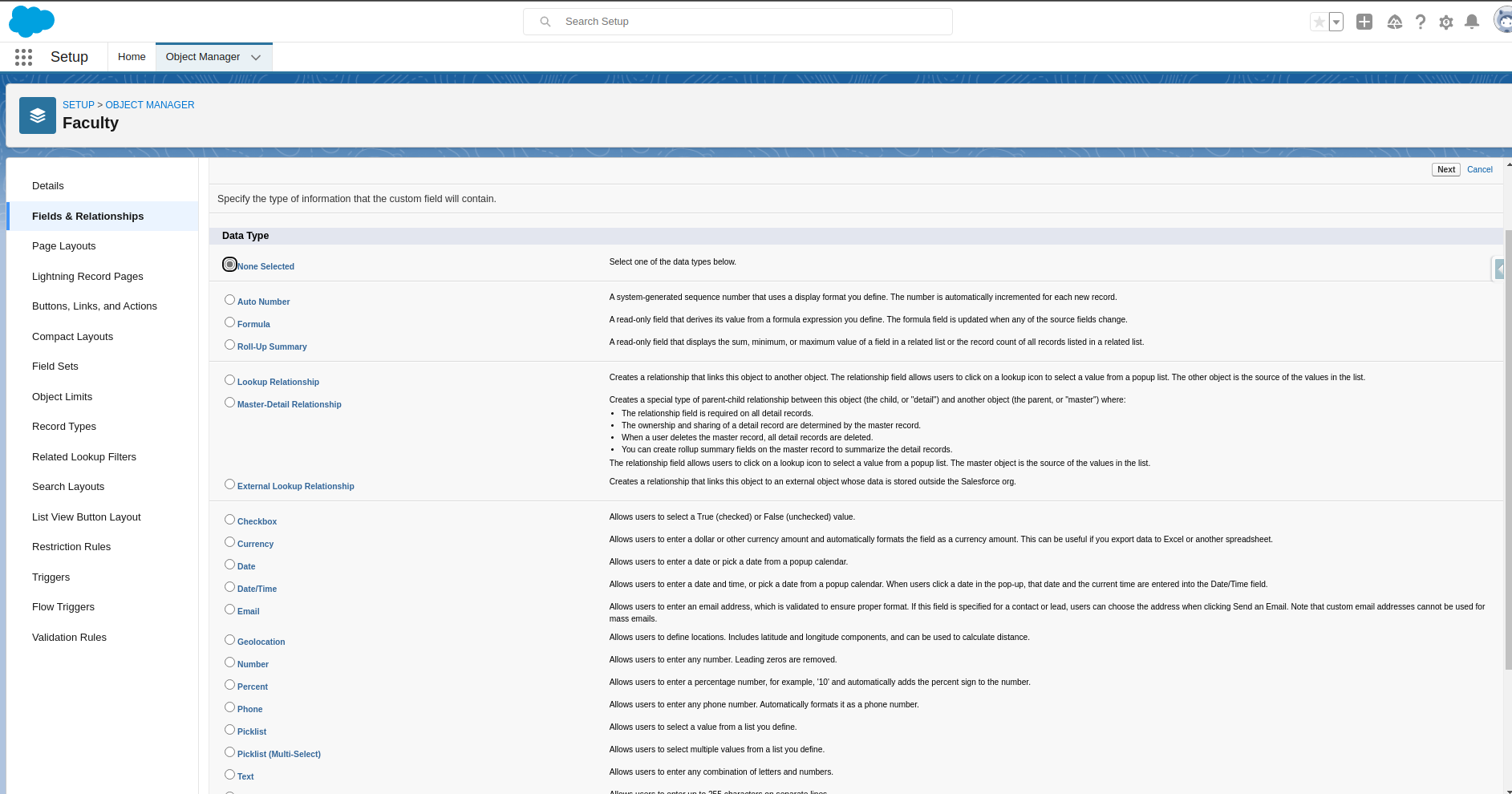
Click on New to create Field and select the field data type that you want to create.
Fill Field Details
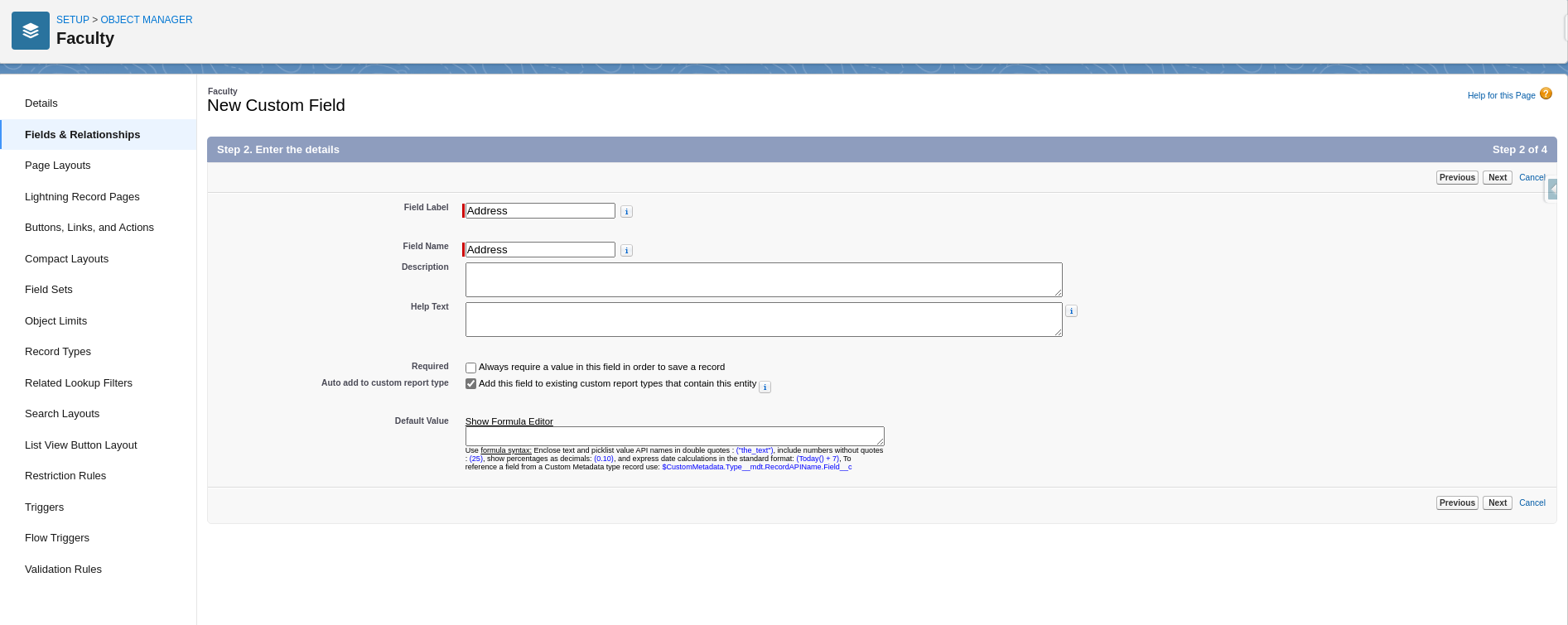
Fill in all required field details
Set Field Level Security & Save
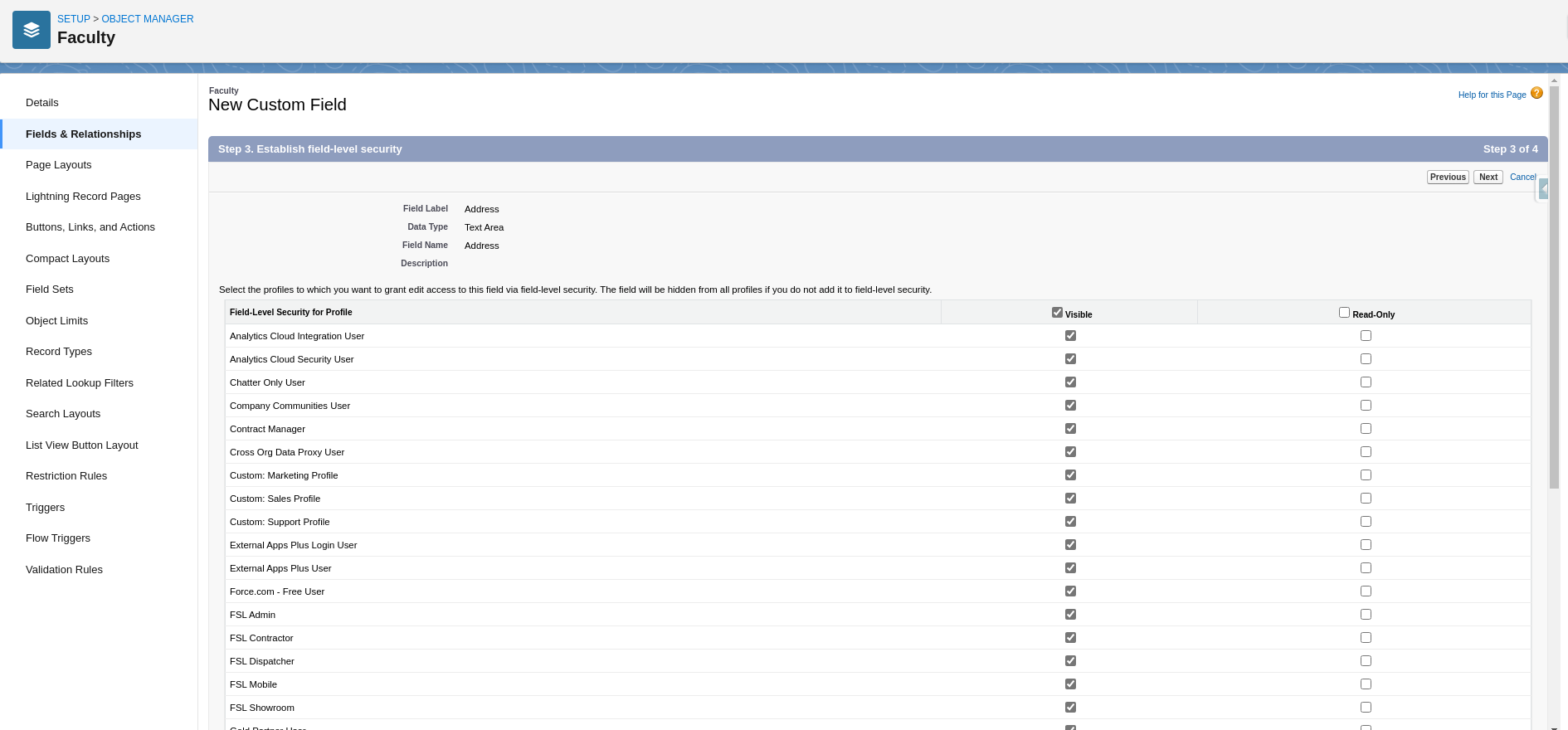
User can Set Field Level Security on each profile and specifies which profile can see this field.
Field Created
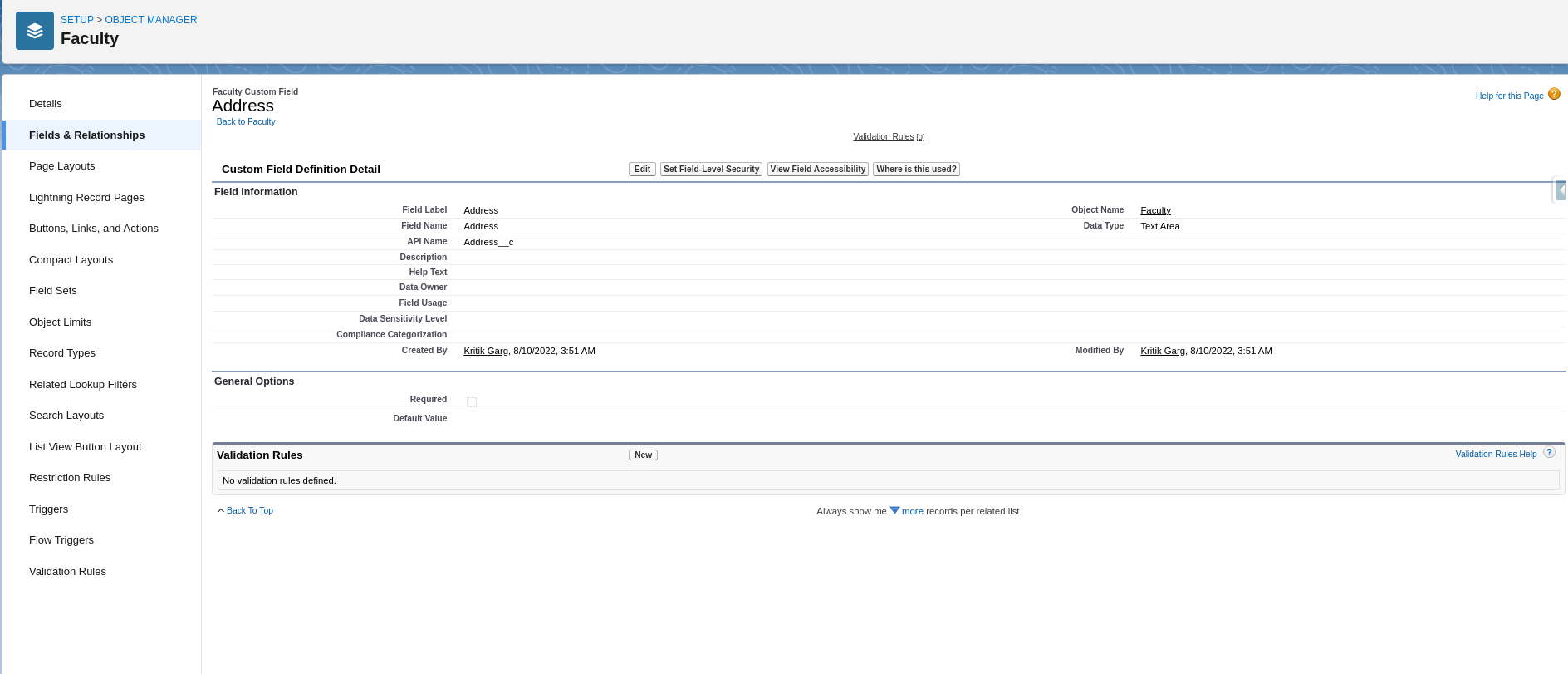
The field created successfully.
How to create Visualforce Tab in Salesforce
How to Create Custom Object Tabs in Salesforce Lightning
Learn More about Lightning object creator
Relationship Between Objects
Relationships make a connection between two objects. It is used to link objects and help to display data about their related objects. To establish a connection between two objects, we have to use relationship fields such as Lookup or master-detail relationship.
In Salesforce, To create a relationship we use the concept of Primary Key and Foreign Key. Primary Key resides on the table which is one in a many-to-one relationship and Foreign Key resides on the table which is many in a many-to-one relationship.
The field is created on the many side object and it is related to the one side object. Before you begin creating relationships first determine the type of relationship that suits your needs.
For Example :
Faculty ⇒ student (Lookup)
Course ⇒ student (Master-detail)
Types of Relationships
In Salesforce, mainly two types of relationships Master-Detail and Lookup Relationship.
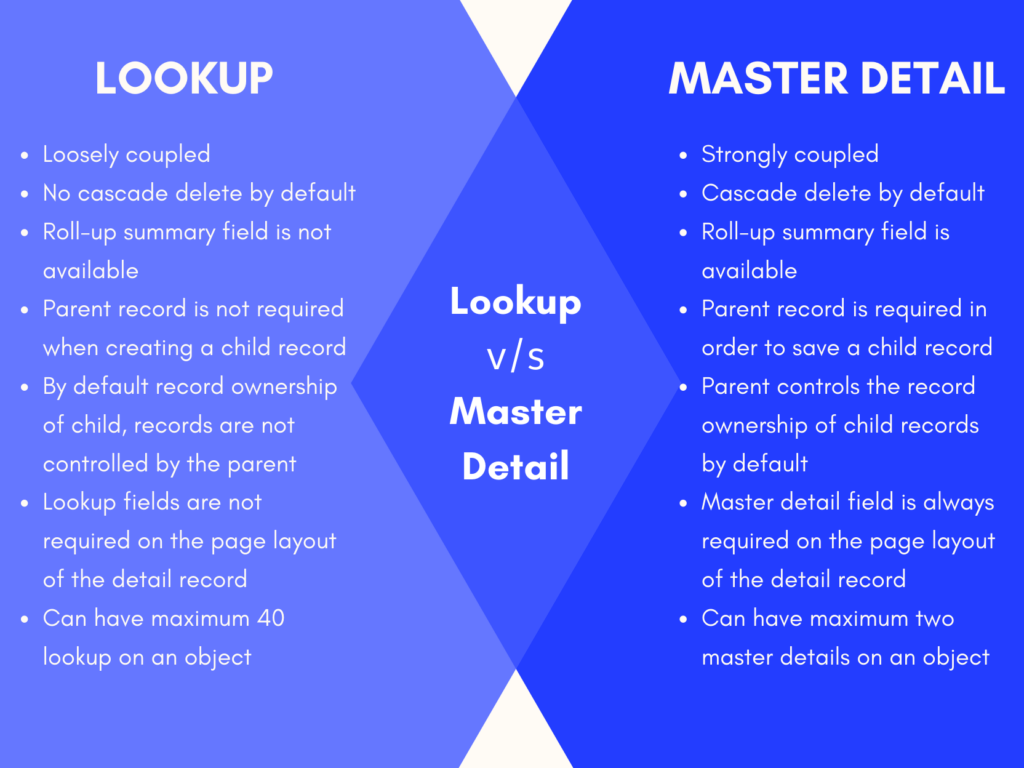
Master-Detail
Master-Detail relationship is used when we want a parent-child relationship or want to control the display of detailed records based on the value in the master record. For example, In college, a student is always linked with the course. if we remove the course then all the related students are also removed. Such a dependency can be achieved through Master-Detail Relationship.
Some Features of Master-Detail Relationship
- If deleting a Master Record then delete automatically all the detail records.
- A detailed record cannot be created without a Master record.
- The permission on the detail record cannot be set. It inherits permission from the master record.
- The detail record also inherits the sharing rule from master records.
- Only two master-detail relationships can be created on one object.
Lookup
The lookup relationship is used to link two objects together. Lookup relationships is similar to master-detail relationships, but it used when objects are only related in some cases. It is a loosely coupled relationship among Salesforce objects, which means even if a parent record gets deleted, the child records remain in the system. Lookup is mostly used in commonly shared data between two objects.
For example, imagine a scenario of a relationship between students and faculty. if any faculty remove then no effect on its related student because any other faculty will be allotted to those students. so such type of relationship comes under the lookup.
Self-relationship
- When an object has a lookup with itself, it is a self-relationship.
- For example, a campaign record can have a Parent Campaign record, This is the best scenario to show how multiple child campaigns relate to the main parent campaign.
Hierarchical relationship
- In Salesforce, only a user object has this type of relationship where we can create a hierarchy of users in the organization.
- For example, a user can have his manager, and his manager may have a senior manage,ment and so on till the CEO level.
External lookup relationship
- An external lookup relationship allows us to link an external object to a parent external object whose data is stored in an external data source. In other words, it allows us to link two external objects
Indirect lookup relationship
- An indirect lookup relationship allows us to link an external object to a standard or custom object.
- We can only create an indirect lookup to an object with a unique external ID field on the parent object that is used to match the records in this relationship.
- While creating an indirect lookup relationship field on an external object, we have to specify the child object field and the parent object field to match and associate records in the relationship.
- For example, we can display a related list of payments from the ERP external record with matching external IDs on the account object.
How To Create a Relationship Between Two Objects
Go to Setup & Open Object Manager
Select Object & Open
Go to Field & Relationships Then Click On New
Select Relationship Data Type
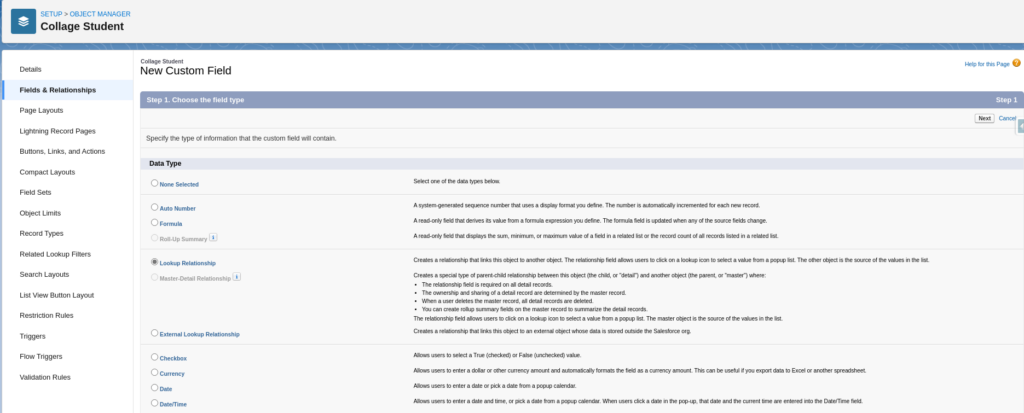
Choose Related Object
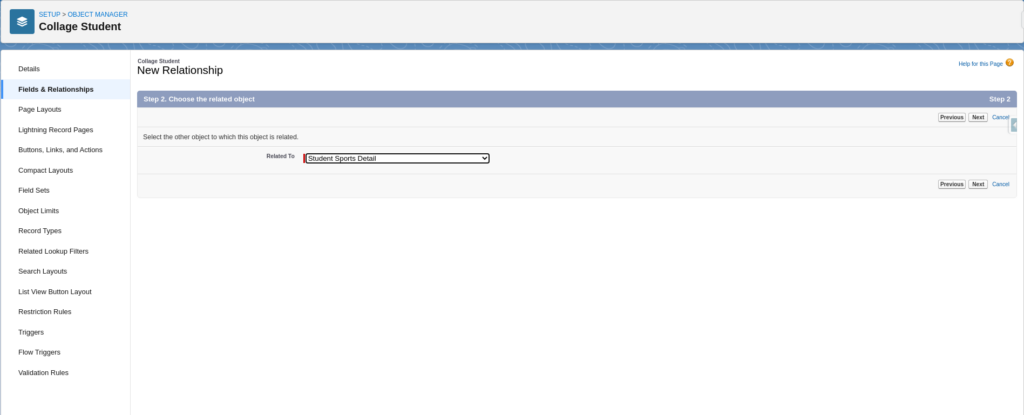
Fill Relationship Details
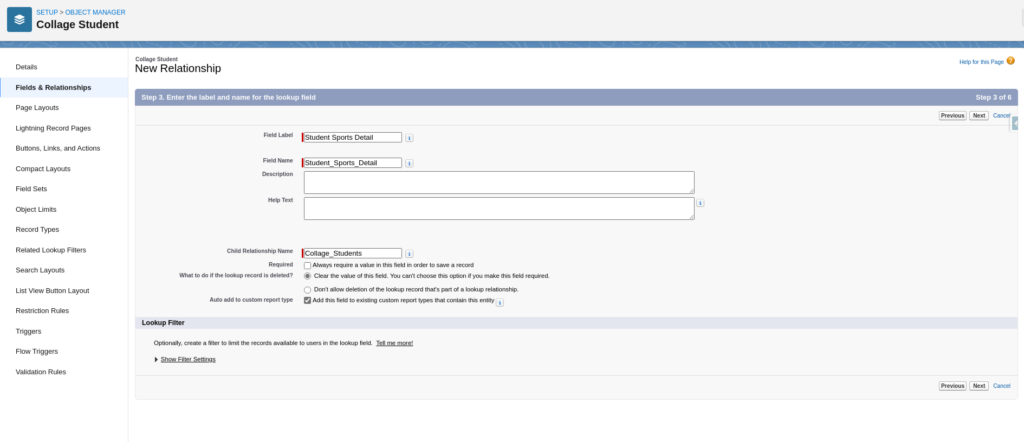
Set Field Level Security For Each Profile
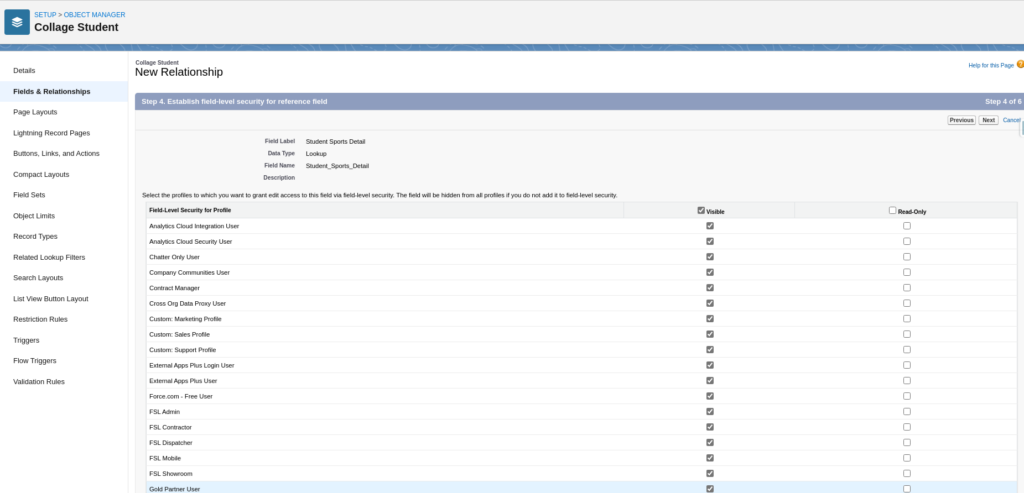
Add Field To Page Layouts
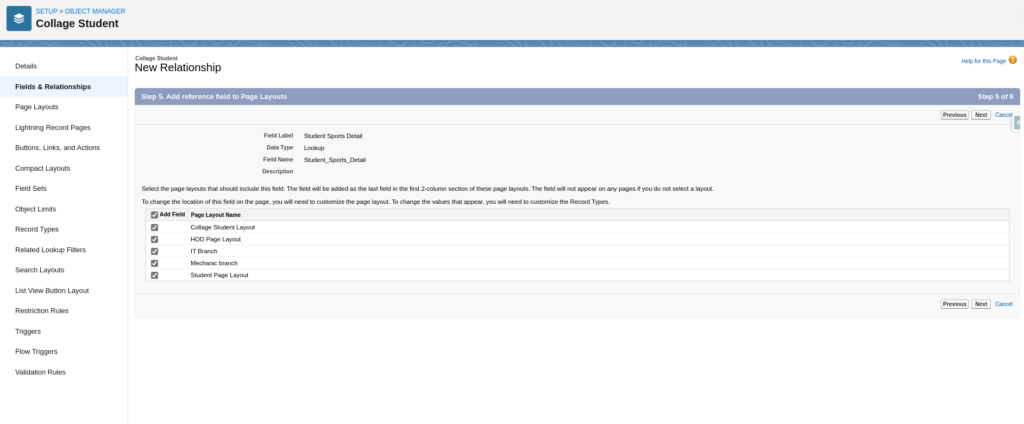
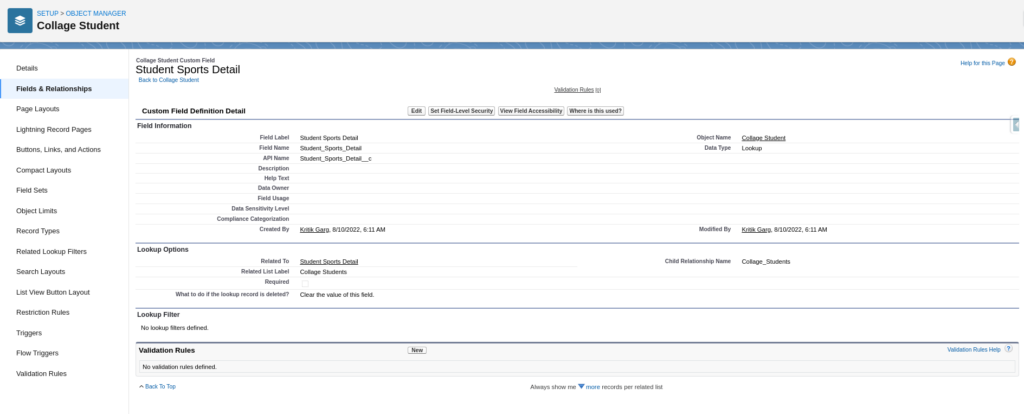
This Screen Confirmed Relationship Field Created
Difference B/W Lookup & Master-Detail Relationship
| Lookup relationship | Master-detail relationship |
|---|---|
| Loosely coupled. | Strongly coupled. |
| The roll-up summary field is not available. | The roll-up summary field is available. |
| A parent record is not required when creating a child record. | A parent record is required in order to save a child record. |
| Lookup fields are not required on the page layout of the detail record but if you make them a required field, it is advised! | Master-detail field is always required on the page layout of the detail record (because of the point above). |
| Standard object records can be on the detail side of a custom object in a lookup relationship. | Standard object records cannot be a child. |
| By default record ownership of child, records are not controlled by the parent. | The parent controls the record ownership of child records. |
| You can have a child record without a parent. | You cannot have a child record without a parent. |
| You can have a maximum of 40 lookups on an object. | You can have a maximum of two master details on an object. |
| No cascade delete by default. | Cascade delete by default. |
Other terms related to Salesforce Object
Junction object in Salesforce
Salesforce provides multiple types of relationships to connect two objects together. You may be familiar with the two main relationships as master-detail and lookup relationships. These allow users to create a parent-child relationship which is sometimes referred to as one-to-many relationships which means there is one parent and multiple child records. But, what happens when we need to create many too many relationships?
In this case, we need to create a junction object to establish many to many relationships between two objects. To create a junction, first, we need to create a custom object which establishes a connection with those two objects via master-detail or lookup relationship.
Example of Junction object :
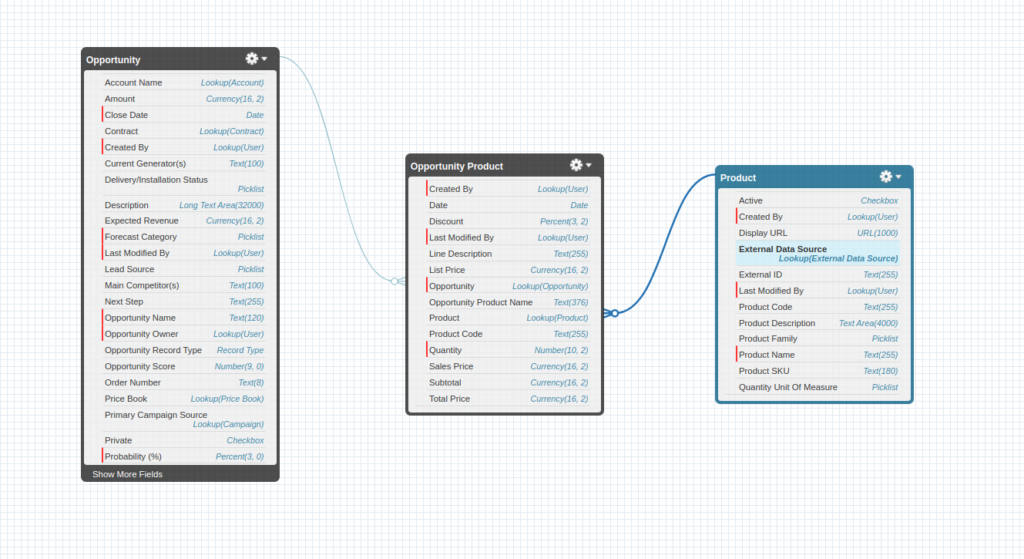
We have an example of two standard objects Opportunity and product. Both objects has many to many relationship. An opportunity can have more than one product as well as a product can be added to more than one opportunity. So this type of scenario establishes by the junction object.
As shown below image a junction object (opportunity product ) is created for opportunity and product.
Record Types In Salesforce
Salesforce Record Types allow us to create functionality on records that display different picklist values and page layouts to users. The record type is like object slicing, which that means with the help of Record type objects can divide into multiple forms.
Administrators can add record types with profiles so that different types of users can see different picklist values and page layouts on the record’s detail page.
A profile can have only one-page layout but, if we want to add multiple page layouts on the profile then we can do it with the help of Record type.
Use Of Record Types
- The biggest use of Record type is that In the same profile we can show different-different types of information to a different users on record creation with help of this.
- We can assign multiple page layouts for a single object according to requirements.
- For example, On the creation of a student record, we can show subjects based on student streams. First, create a pick list for subjects & assign different-different picklist values to different page layouts with the help of Record type.
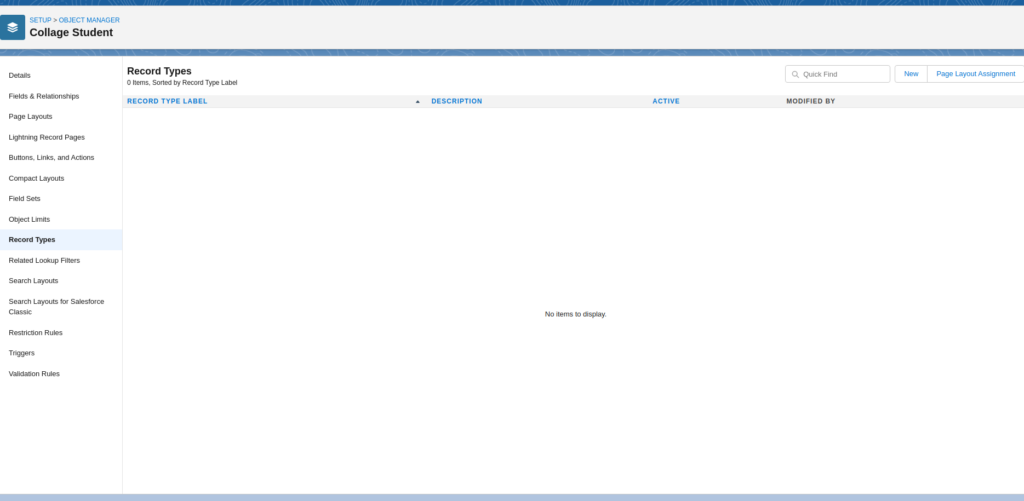
How To Create Record Type
Go to Setup & Open Object Manager
Select Object & Open
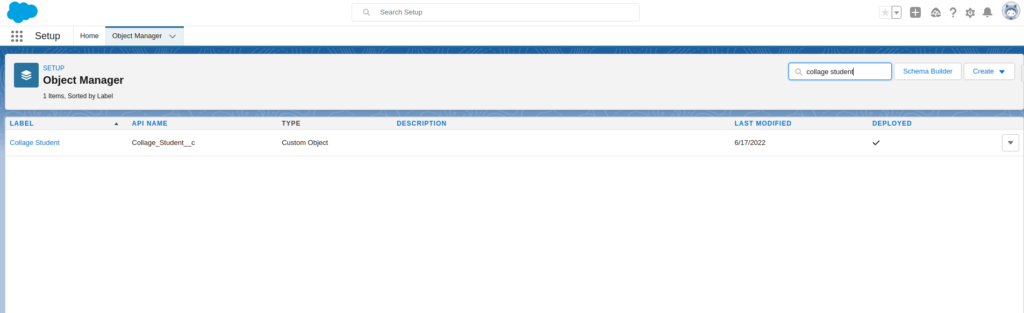
Go to Page Layout & Create Page Layout for IT branch
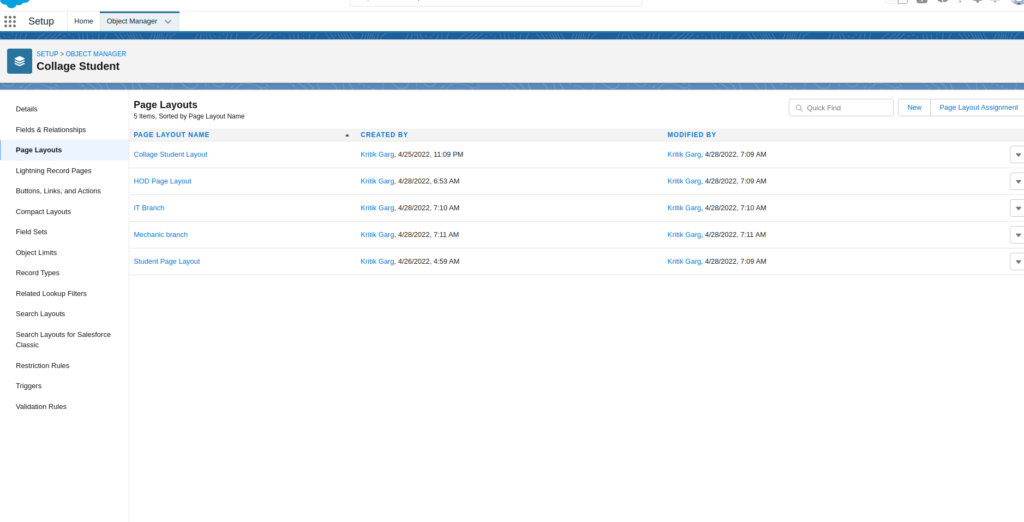
Go to Record Types Then Click On New
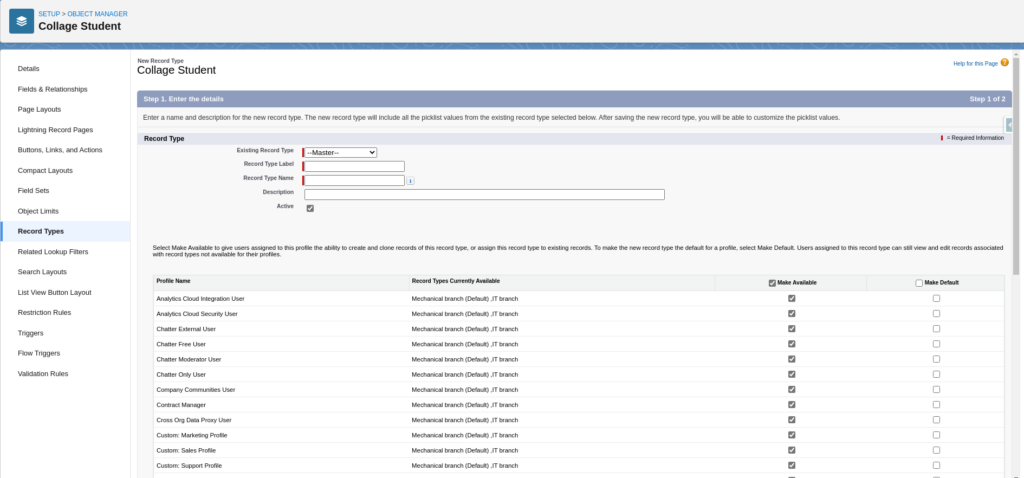
Fill Record Type Details & Make Available For Profile
Assign Page Layout
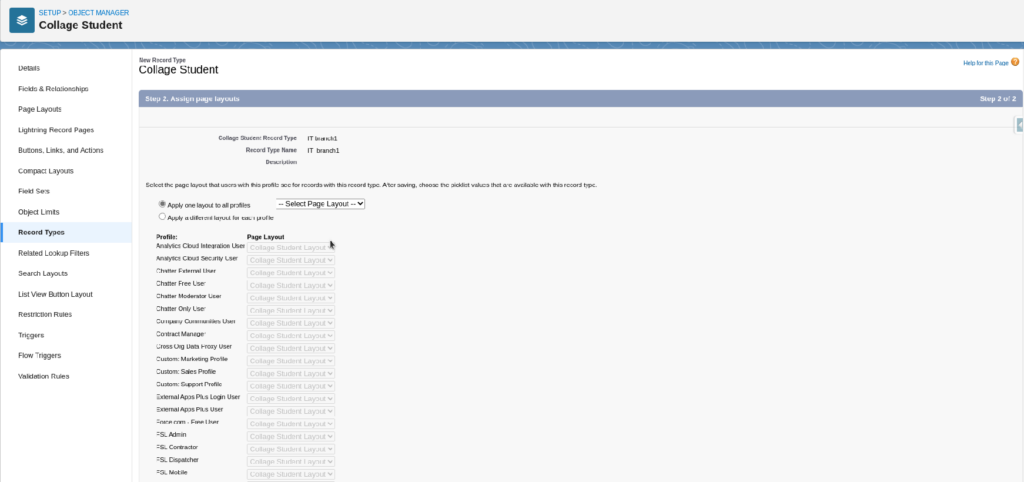
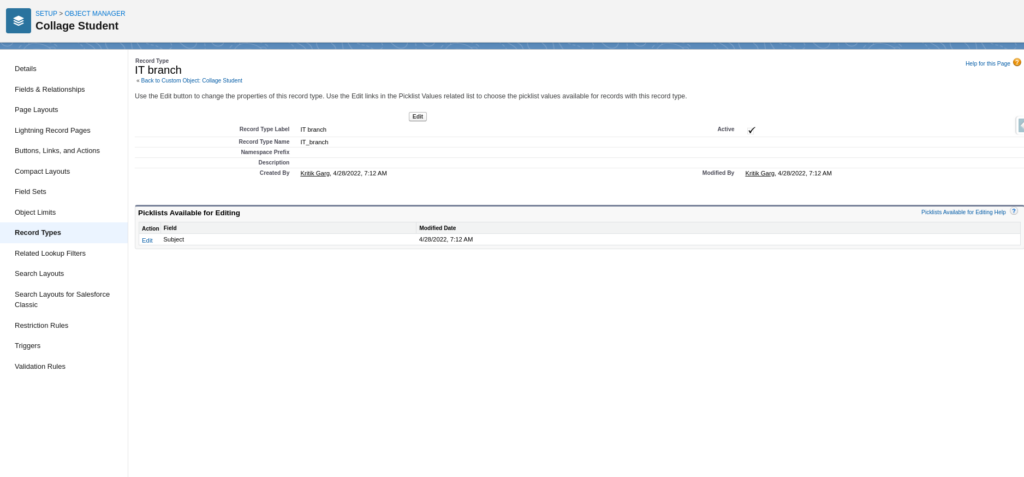
This Screen Confirmed Record Type Created
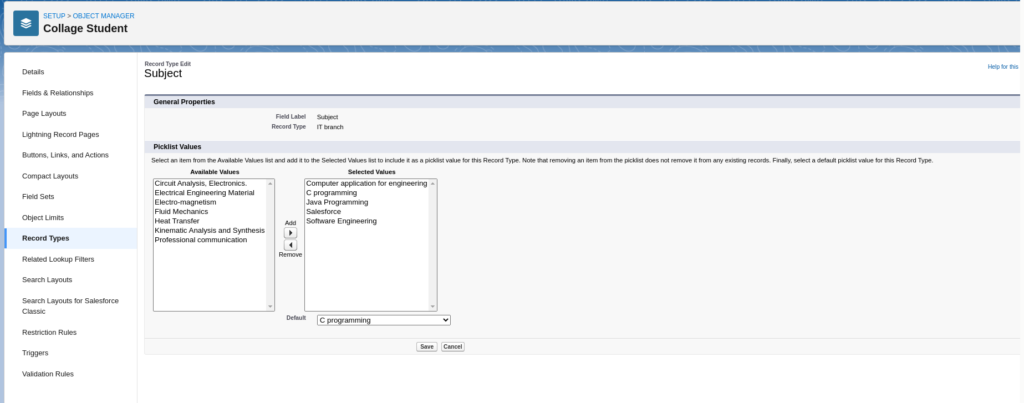
Arrange Picklist Values (Select subject value according to branch)
Go To Student Object, Select Record Type & Create New Record
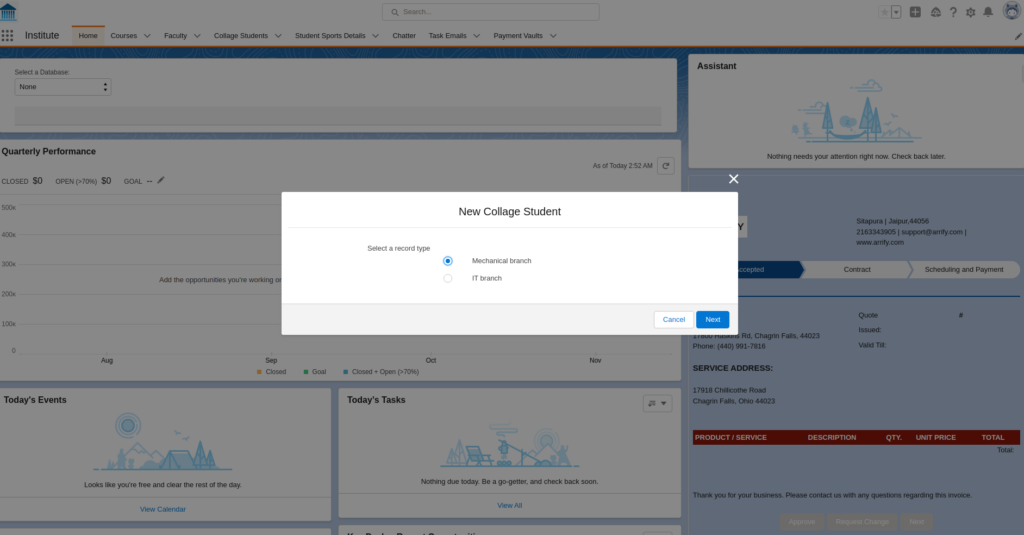
Showing Subject Values Based On Stream With Help Of Record Type
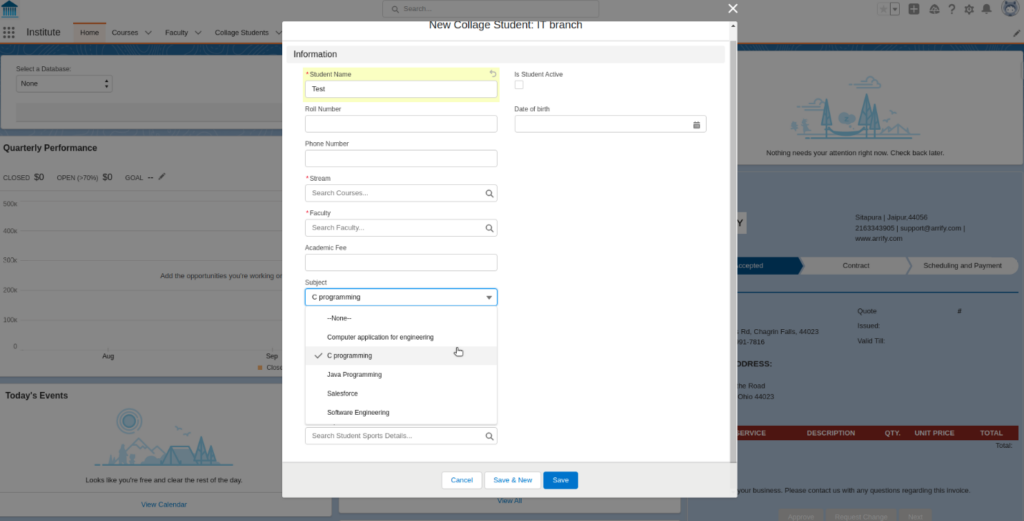
Learn More about Record Types in Salesforce.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Salesforce objects are the building blocks of the Salesforce platform, and they can be divided into standard objects, custom objects, external objects, and big objects.
A field is a specific element within an object that stores a specific piece of data. Fields can be standard or custom, and they have different data types. To create a custom object and field, you can use the object manager in Setup.
There are also different types of relationships between objects, such as Master-Detail and Lookup, which can be created through the object manager. Other terms related to Salesforce objects include junction objects and record types, which can be used to further customize the data stored within the platform.
Overall, Salesforce objects and fields play an essential role in organizing and managing data within the Salesforce platform.